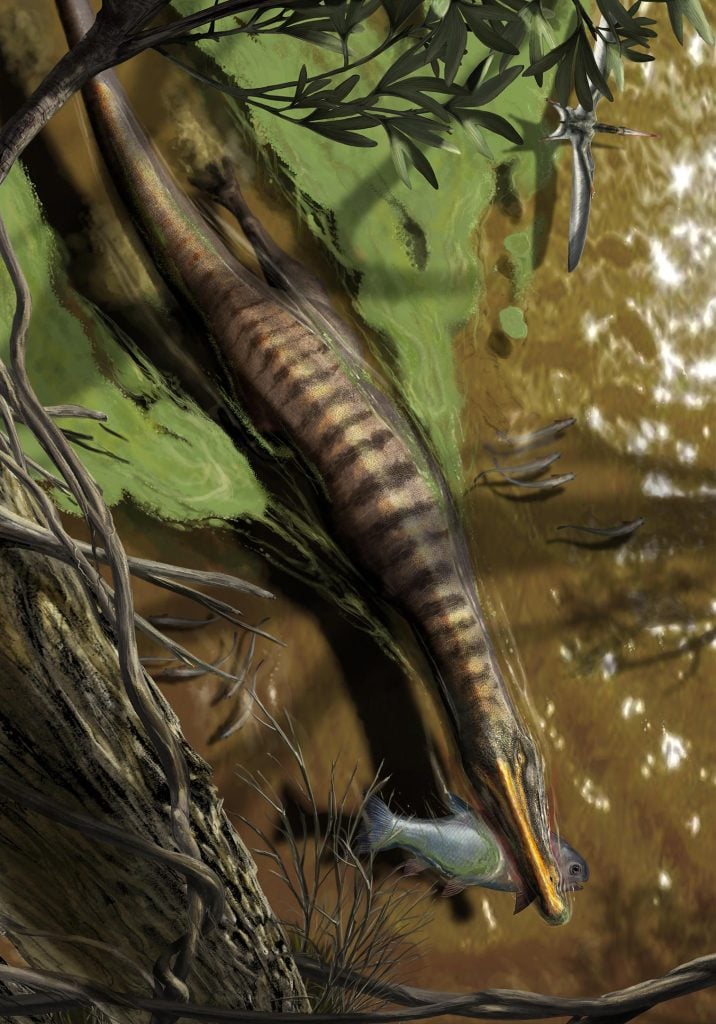
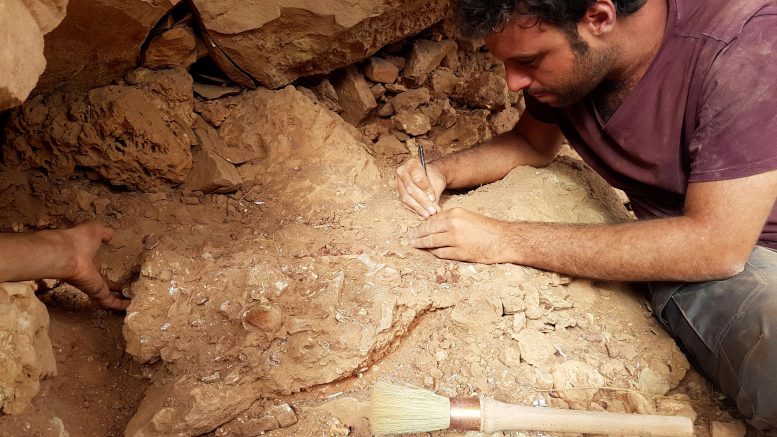
Спинозавр, самый длинный из известных хищных динозавров, открывает свои удлиненные челюсти, усеянные коническими зубами, чтобы поймать пилу. Вопреки предыдущим предположениям, это животное не было похожим на болотную цаплю — это был «речной зверь», активно преследующий добычу в обширной речной системе, расположенной на территории современной Северной Африки. Плотные кости в скелете спинозавра убедительно свидетельствуют о том, что он долгое время находился под водой. Кредит: Дэвид Бонадонна
Его близкий родственник Барионикс, возможно, тоже плавал, но Зухомим, возможно, передвигался вброд, как цапля.
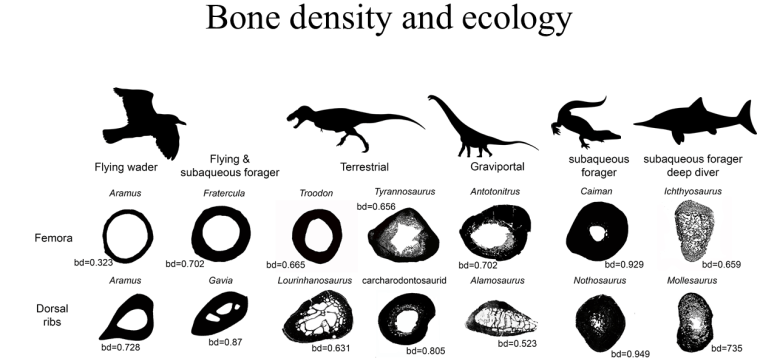
Спинозавр Это крупнейший из когда-либо обнаруженных плотоядных динозавров — больше, чем Ти-Рекс— Но метод их ловли был предметом споров на протяжении десятилетий. Трудно угадать поведение животного, о котором мы знаем только по окаменелостям; Основываясь на его скелете, некоторые ученые предположили, что Спинозавр Он умеет плавать, но другие думают, что он бродит по воде, как цапля. Поскольку изучения анатомии спинозавридных динозавров было недостаточно, чтобы разгадать тайну, группа палеонтологов публикует новое исследование в природа Он использует другой подход: проверяет плотность их костей. Анализируя плотность костей спинозавров и сравнивая их с другими животными, такими как пингвины, бегемоты и крокодилы, команда обнаружила, что Спинозавр и его родственники Барионикс У них были плотные кости, которые, вероятно, позволяли им погружаться под воду для охоты. Между тем, другой родственный динозавр по имени Шомем Его кости были легче по весу, что затруднило бы плавание, поэтому он, скорее всего, вместо этого будет переходить вброд или проводить больше времени на суше, как другие динозавры.

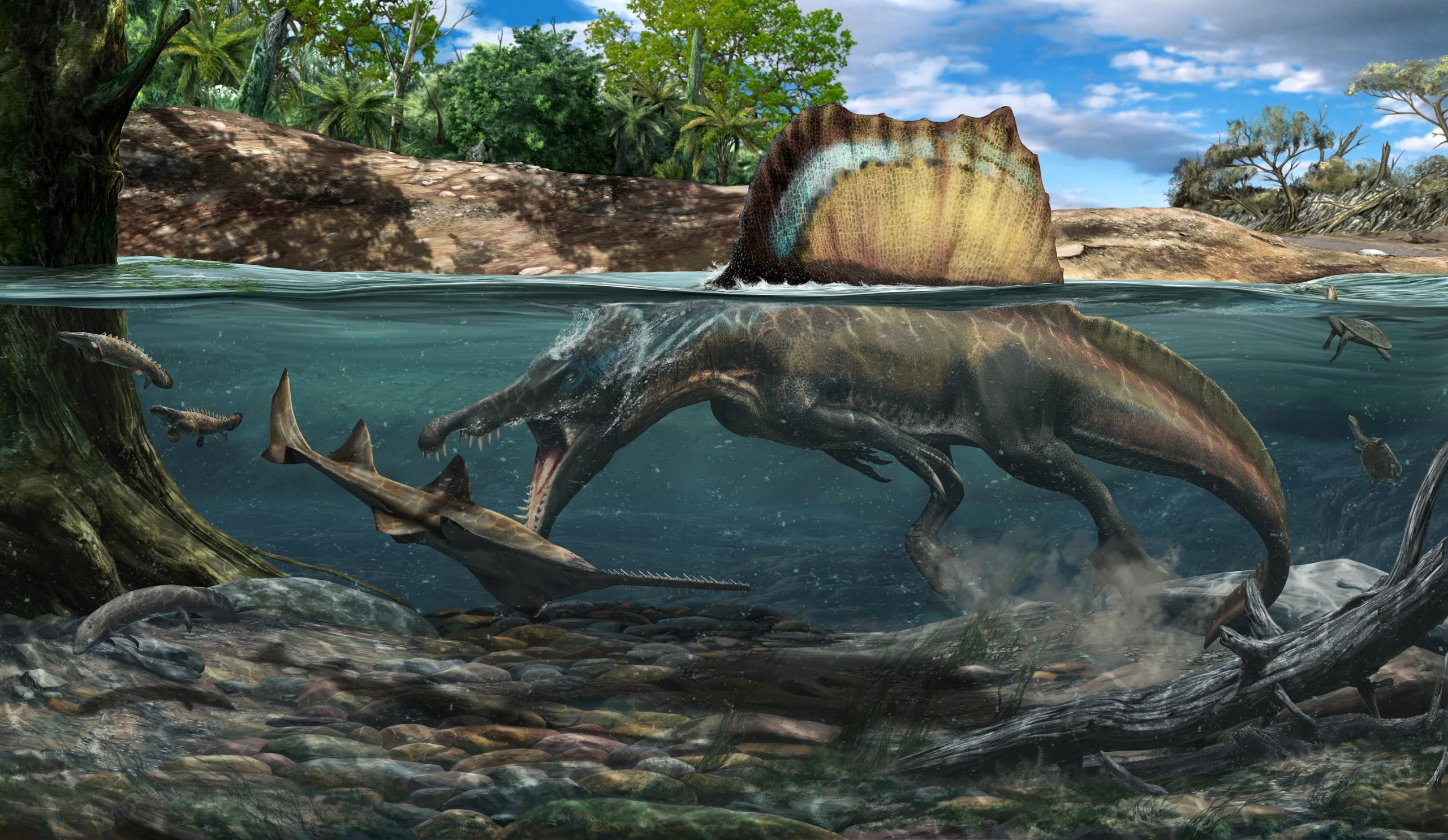
Барионикс из Суррея в Англии переплывает древнюю реку с рыбой в пасти. Как и у его более крупного африканского родственника спинозавра, у барионикса были плотные кости, что указывает на то, что он также проводил большую часть своего времени под водой. Ранее считалось, что он менее водной, чем его пустынный родственник. Кредит: Дэвид Бонадонна
— говорит Маттео Фабри, научный сотрудник Полевого музея и ведущий автор учебного пособия. природа. «Другие исследования были сосредоточены на интерпретации анатомии, но ясно, что наличие противоположных интерпретаций в отношении одних и тех же костей уже является явным признаком того, что это, вероятно, не лучшие наши прокси для вывода об экологии вымерших животных».
Вся жизнь изначально произошла из воды, и у большинства групп наземных позвоночных есть органы. -водные бегемоты. Среди птиц есть пингвины и бакланы. Рептилии включают крокодилов, крокодилов, морских игуан и морских змей. Долгое время нептичьие динозавры (динозавры, не разветвившиеся на птиц) были единственной группой, у которой не было никаких водных обитателей. Ситуация изменилась в 2014 году, когда файл Спинозавр Скелет, описанный Низаром Ибрагимом в[{» attribute=»»>University of Portsmouth.
Scientists already knew that spinosaurids spent some time by water—their long, croc-like jaws and cone-shaped teeth are similar to other aquatic predators’, and some fossils had been found with bellies full of fish. But the new Spinosaurus specimen described in 2014 had retracted nostrils, short hind legs, paddle-like feet, and a fin-like tail: all signs that pointed to an aquatic lifestyle. But researchers have continued to debate whether spinosaurids actually swam for their food or if they just stood in the shallows and dipped their heads in to snap up prey. This continued back-and-forth led Fabbri and his colleagues to try to find another way to solve the problem.
“The idea for our study was, okay, clearly we can interpret the fossil data in different ways. But what about the general physical laws?” says Fabbri. “There are certain laws that are applicable to any organism on this planet. One of these laws regards density and the capability of submerging into water.”

Simone Maganuco (middle), Davide Bonadonna (right) and lead author Matteo Fabbri (left) organizing fossils at night. Credit: Nanni Fontana
Across the animal kingdom, bone density is a tell in terms of whether that animal is able to sink beneath the surface and swim. “Previous studies have shown that mammals adapted to water have dense, compact bone in their postcranial skeletons,” says Fabbri. Dense bone works as buoyancy control and allows the animal to submerge itself.
“We thought, okay, maybe this is the proxy we can use to determine if spinosaurids were actually aquatic,” says Fabbri.
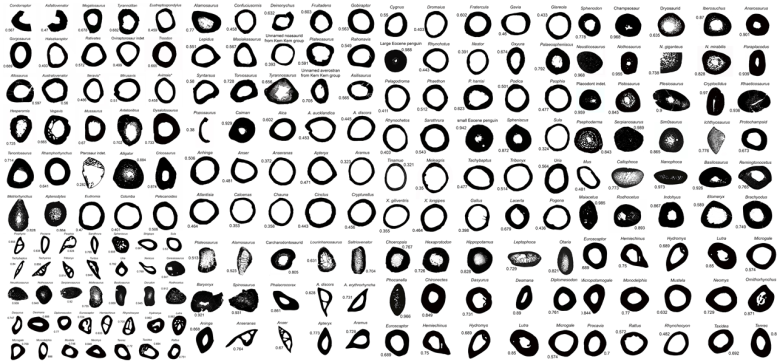
Fabbri and his colleagues, including co-corresponding authors Guillermo Navalón at Cambridge University and Roger Benson at Oxford University, put together a dataset of femur and rib bone cross-sections from 250 species of extinct and living animals, both land-dwellers and water-dwellers. The researchers compared these cross-sections to cross-sections of bone from Spinosaurus and its relatives Baryonyx and Suchomimus. “We had to divide this study into successive steps,” says Fabbri. “The first one was to understand if there is actually a universal correlation between bone density and ecology. And the second one was to infer ecological adaptations in extinct taxa” Essentially, the team had to show a proof of concept among animals that are still alive that we know for sure are aquatic or not, and then applied them to extinct animals that we can’t observe.
When selecting animals to include in the study, the researchers cast a wide net. “We were looking for extreme diversity,” says Fabbri. “We included seals, whales, elephants, mice, hummingbirds. We have dinosaurs of different sizes, extinct marine reptiles like mosasaurs and plesiosaurs. We have animals that weigh several tons, and animals that are just a few grams. The spread is very big.”
This menagerie of animals revealed a clear link between bone density and aquatic foraging behavior: animals that submerge themselves underwater to find food have bones that are almost completely solid throughout, whereas cross-sections of land-dwellers’ bones look more like donuts, with hollow centers. “There is a very strong correlation, and the best explanatory model that we found was in the correlation between bone density and sub-aqueous foraging. This means that all the animals that have the behavior where they are fully submerged have these dense bones, and that was the great news,” says Fabbri.
When the researchers applied spinosaurid dinosaur bones to this paradigm, they found that Spinosaurus and Baryonyx both had the sort of dense bone associated with full submersion. Meanwhile, the closely related Suchomimus had hollower bones. It still lived by water and ate fish, as evidenced by its crocodile-mimic snout and conical teeth, but based on its bone density, it wasn’t actually swimming.
Other dinosaurs, like the giant long-necked sauropods also had dense bones, but the researchers don’t think that meant they were swimming. “Very heavy animals like elephants and rhinos, and like the sauropod dinosaurs, have very dense limb bones, because there’s so much stress on the limbs,” explains Fabbri. “That being said, the other bones are pretty lightweight. That’s why it was important for us to look at a variety of bones from each of the animals in the study.” And while there are limitations to this kind of analysis, Fabbri is excited by the potential for this study to tell us about how dinosaurs lived.
“One of the big surprises from this study was how rare underwater foraging was for dinosaurs, and that even among spinosaurids, their behavior was much more diverse that we’d thought,” says Fabbri.
Jingmai O’Connor, a curator at the Field Museum and co-author of this study, says that collaborative studies like this one that draw from hundreds of specimens, are “the future of paleontology. They’re very time-consuming to do, but they let scientists shed light onto big patterns, rather than making qualitative observations based on one fossil. It’s really awesome that Matteo was able to pull this together, and it requires a lot of patience.”
Fabbri also notes that the study shows how much information can be gleaned from incomplete specimens. “The good news with this study is that now we can move on from the paradigm where you need to know as much as you can about the anatomy of a dinosaur to know about its ecology, because we show that there are other reliable proxies that you can use. If you have a new species of dinosaur and you just have only a few bones of it, you can create a dataset to calculate bone density, and at least you can infer if it was aquatic or not.”
Reference: “Subaqueous foraging among carnivorous dinosaurs” by Matteo Fabbri, Guillermo Navalón, Roger B. J. Benson, Diego Pol, Jingmai O’Connor, Bhart-Anjan S. Bhullar, Gregory M. Erickson, Mark A. Norell, Andrew Orkney, Matthew C. Lamanna, Samir Zouhri, Justine Becker, Amanda Emke, Cristiano Dal Sasso, Gabriele Bindellini, Simone Maganuco, Marco Auditore and Nizar Ibrahim, 23 March 2022, Nature.
DOI: 10.1038/s41586-022-04528-0

«Главный евангелист пива. Первопроходец в области кофе на протяжении всей жизни. Сертифицированный защитник Твиттера. Интернетоголик. Практикующий путешественник».


:quality(70)/cloudfront-eu-central-1.images.arcpublishing.com/irishtimes/X53DY6Q53OGZ2AFC755PEJGYHM.jpg)
:quality(70)/cloudfront-eu-central-1.images.arcpublishing.com/irishtimes/LH232YK2SFGLJJZ57TDTSA77KA.jpg)




More Stories
Огромное доисторическое морское чудовище ростом выше двух автобусов было обнаружено после того, как 11-летняя британская девочка нашла окаменелости на пляже Сомерсет.
Пациент-ориентированная интегративная и альтернативная терапия в неврологии: Кэролин Бернштейн, доктор медицинских наук
Раскройте тайны космической химии